I know how I’m SUPPOSED to read it, but when I see this I can’t help but imagine a conversation like…
“What shall we call our car wash?”
/waves hand/ “I dunno.”
Especially outside of urban centres, and especially if you’re on foot, OpenStreetMap is way better than Google Maps, Bing Maps, Apple Maps, or what-have-you.
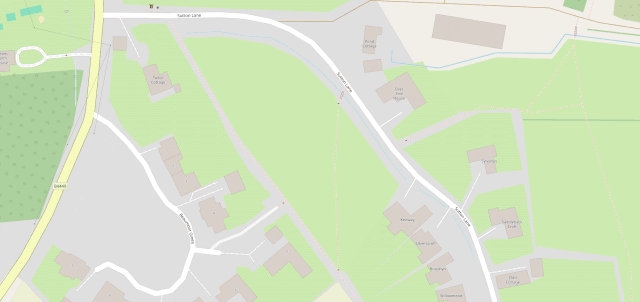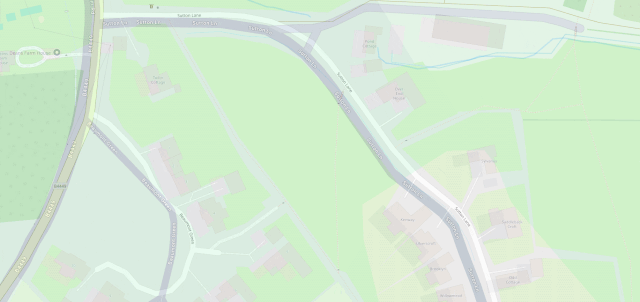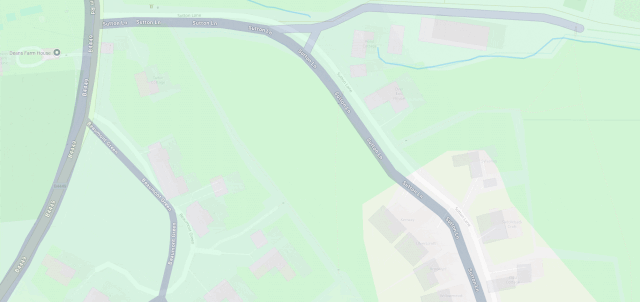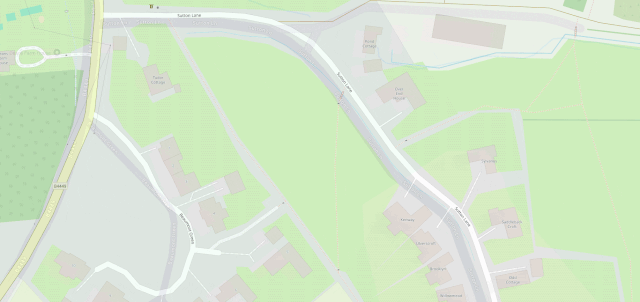
OpenStreetMap is especially good for walkers, with its more-comprehensive coverage of public footpaths as well as the ability to drill-down for accessibility information: whether a path ends in a gate or a stile matters a lot if you can’t climb the latter (or you’re walking with a small-but-muddy dog who’ll need lifting over).
Sure, you don’t get (as much) street view photography. But how often do you use that, anyway?1
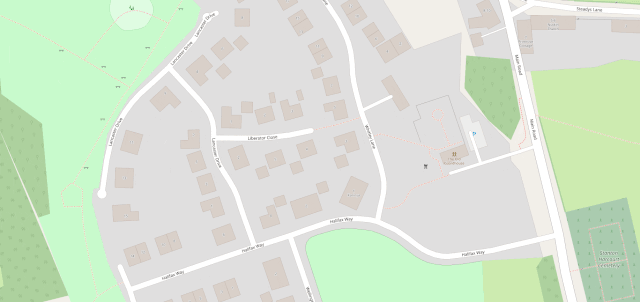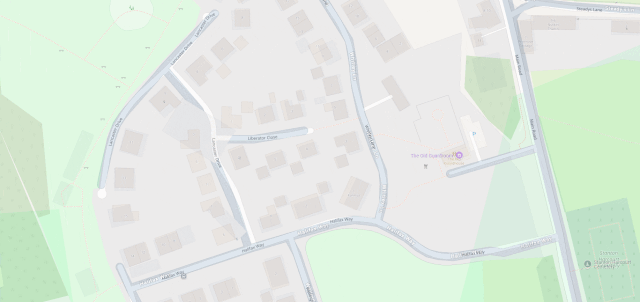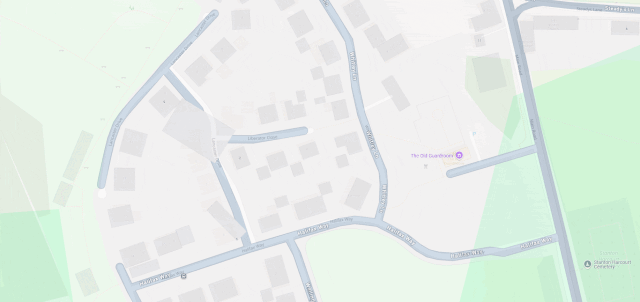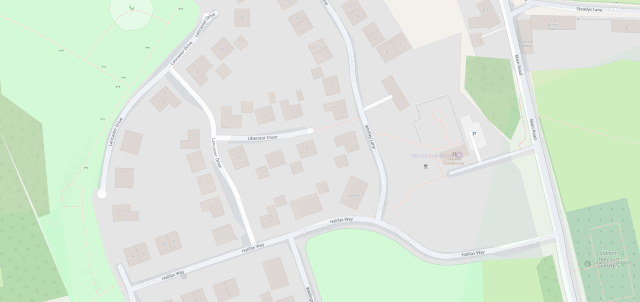
I’ve heard it argued that OpenStreetMap, with its Wikipedia-like “anybody can edit it” model, cannot be relied upon. And sure, if you’re looking for an “official” level of accuracy and the alternative is an Ordinance Survey map, then that’s what you should go for.
But there’s nothing specific to, say, Google Maps that makes it fundamentally more “accurate” for most2 geographic features than OpenStreetMap. The vast of cartographic data on Google Maps is produced by humans, looking at satellite photos, and then tracing the features on them, probably with AI assistance. And the vast majority of cartographic data on OpenStreetMap is produced… exactly the same way, although without the AI “helping”.
Google Maps has mistakes, just like every map3. And it’s got trap streets, like most commercially-produced maps (including the Ordinance Survey). Google Maps’ mistakes tend to be made by somebody on the other side of the world from the feature, doing a bad job of tracing what they think might be a road… while OpenStreetMaps’ mistakes are for the most part omissions in areas that are under-explored by local contributors. And there are plenty of areas – like those near where I live, especially if you’re on foot – where the latter mistakes are much less-troublesome.
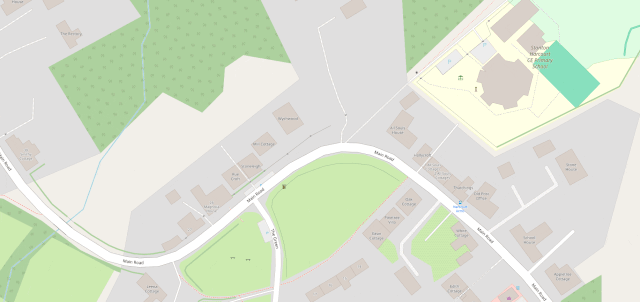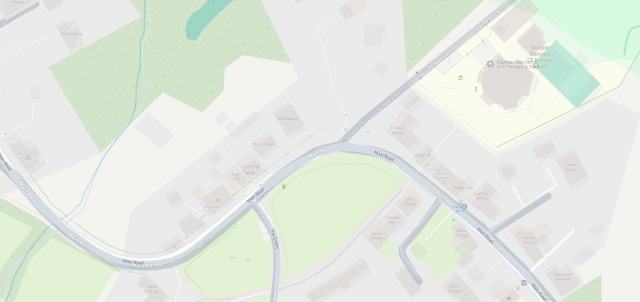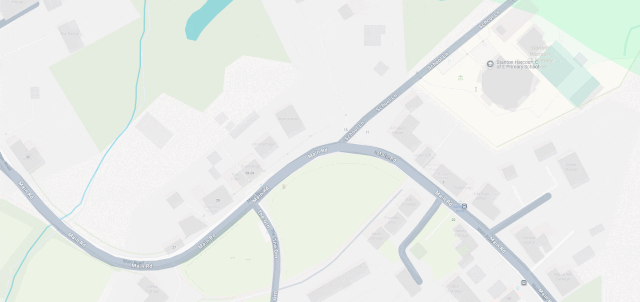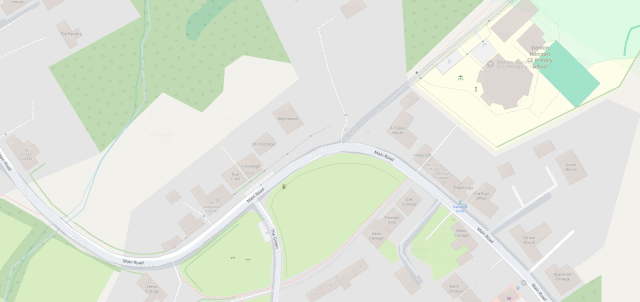
I fixed a couple of omissions on OpenStreetMap just earlier today. While I was out walking the dog, earlier, I added the names of two houses whose identities weren’t specifically marked on the map, and I added detail to the newly-constructed Deansfield estate. Google Maps shows there being only two houses on Deansfield Estate, among other inaccuracies, even though they’ve got up-to-date aerial and street photography.
Google Maps is fine if you want to drive to Sheffield, you need public transport connections to Plymouth4, or you’re looking for a restaurant nearby and you want the data about them to be accurate. But next time you’re walking somewhere, or when you’re looking for a specific address… I’d suggest you give OpenStreetMap a go. You might be pleasantly surprised.
1 I say that as somebody who uses street view and satellite photography a more than average amount, for geohashing purposes. But I can switch mapping software on-the-fly; nobody’s stopping me looking at “ostrich” photos when I need them.
2 The place that Google Maps really beats OpenStreetMap, in my mind, is in the integration of its business directory. If you search for a business in Google Maps, you’ll probably find it and get reasonably-accurate opening hours and contact details. But that’s a factor of two things: the Google My Business directory, and – more importantly – the popularity of the application and the fact that the mobile app “nudges” people to check on the places around them. By the way: if you want to contribute to making maps better in that way without becoming an unpaid researcher working to line Google’s pockets, StreetComplete is an app that helps fill-out business and related information on OpenStreetMap!
3 Google Maps used to show Vauxhall tube station on entirely the wrong side of the River Thames, for example.
4 Public transport’s another thing Google Maps does very well.




What do you reckon? Is he trying to go for a domination victory without ever saying “MY THREATS ARE BACKED BY NUCLEAR WEAPONS!”? His track record shows that he’s arrogant enough to think that the strategy of simply renaming things until they’re yours is actually viable!
After I saw Mexico’s response to Google following Trump’s lead in renaming the Gulf of Mexico, this stupid comic literally came to me in a dream.
Adapts screenshots from Sid Meier’s Civilization (1991 DOS version), public domain assets from
OpenGameArt.org, and AI-assisted images of world leaders on account of the fact that if I drew pixel-art world leaders without assistance then
you’d be even less-likely to be able to recognise them.
Over the last six years I’ve been on a handful of geohashing expeditions, setting out to functionally-random GPS coordinates to see if I can get there, and documenting what I find when I do. The comic that inspired the sport was already six years old by the time I embarked on my first outing, and I’m far from the most-active member of the ‘hasher community, but I’ve a certain closeness to them as a result of my work to resurrect and host the “official” website. Either way: I love the sport.

But even when I’ve not been ‘hashing, it occurs to me that I’ve been tracking my location a lot. Three mechanisms in particular dominate:
If I could mine all of that data, I might be able to answer the question… have I ever have accidentally visited a geohashpoint?
Let’s find out.
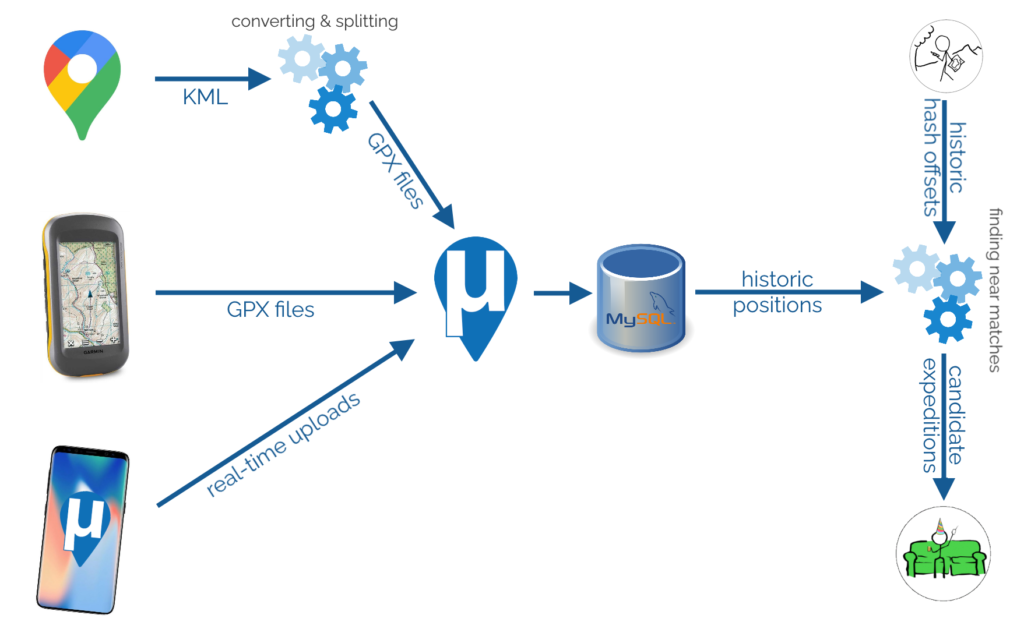
To begin with, I needed to get all of my data into μLogger. The Android app syncs to it automatically and uploading from my GPSr was simple. The data from Google Takeout was a little harder.
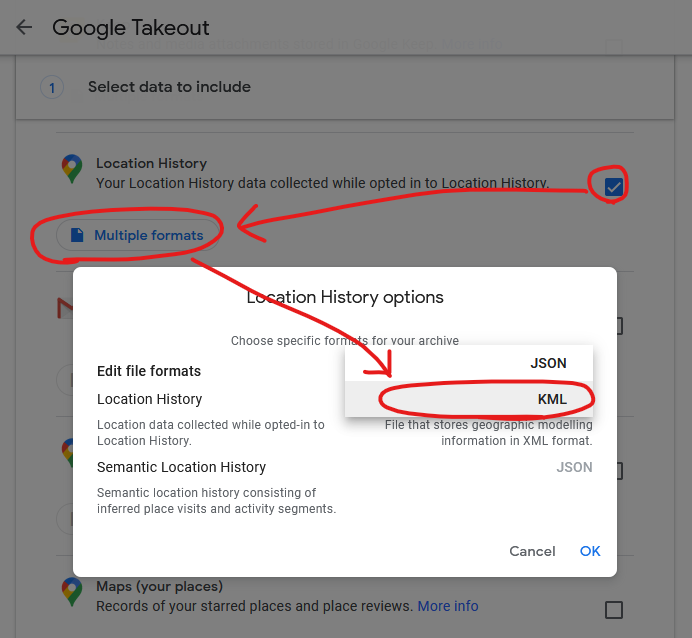
I found a setting in Google Takeout to export past location data in KML, rather than JSON, format. KML is understood by GPSBabel which can convert it into GPX. I can “cut up” the resulting GPX file using a little grep-fu (relevant xkcd?) to get month-long files and import them into μLogger. Easy!
Well.. μLogger’s web interface sometimes times-out if you upload enormous files like a whole month of Google Takeout logs. So instead I wrote a Nokogiri script to convert the GPX into SQL to inject directly into μLogger’s database.
Next, I got a set of hashpoint offsets. I only had personal positional data going back to around 2010, so I didn’t need to accommodate for the pre-2008 absence of the 30W time zone rule. I’ve had only one trip to the Southern hemisphere in that period, and I checked that manually. A little rounding and grouping in SQL gave me each graticule I’d been in on every date. Unsurprisingly, I spend most of my time in the 51 -1 graticule. Adding (or subtracting, for the Western hemisphere) the offset provided the coordinates for each graticule that I visited for the date that I was in that graticule. Nice.
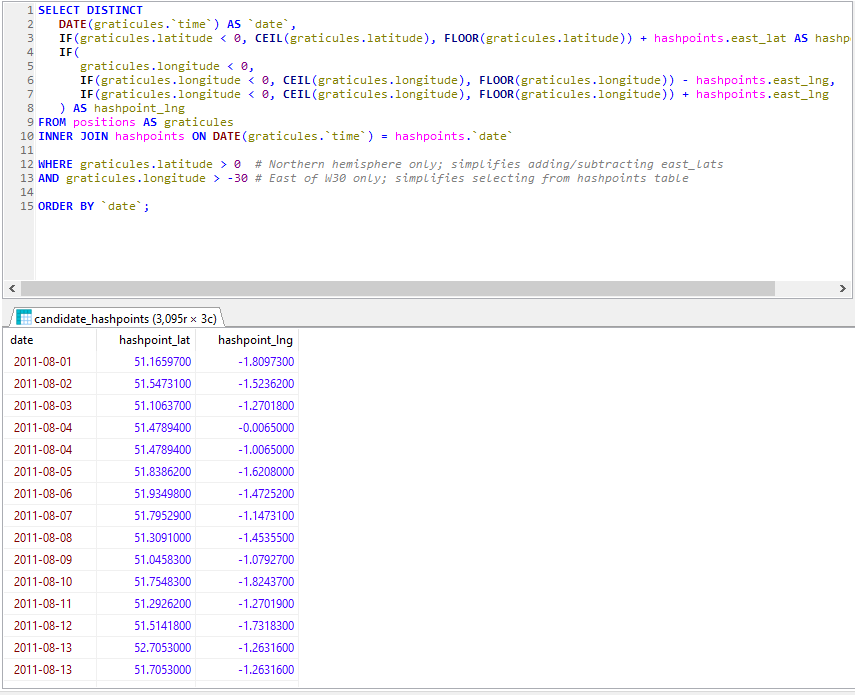
The correct way to find the proximity of my positions to each geohashpoint is, of course, to use WGS84. That’s an easy thing to do if you’re using a database that supports it. My database… doesn’t. So I just used Pythagoras’ theorem to find positions I’d visited that were within 0.15° of a that day’s hashpoint.
Using Pythagoras for geopositional geometry is, of course, wrong. Why? Because the physical length of a “degree” varies dependent on latitude, and – more importantly – a degree of latitude is not the same distance as a degree of longitude. The ratio varies by latitude: only an idealised equatorial graticule would be square!
But for this case, I don’t care: the data’s going to be fuzzy and require some interpretation anyway. Not least because Google’s positioning has the tendency to, for example, spot a passing train’s WiFi and assume I’ve briefly teleported to Euston Station, which is apparently where Google thinks that hotspot “lives”.
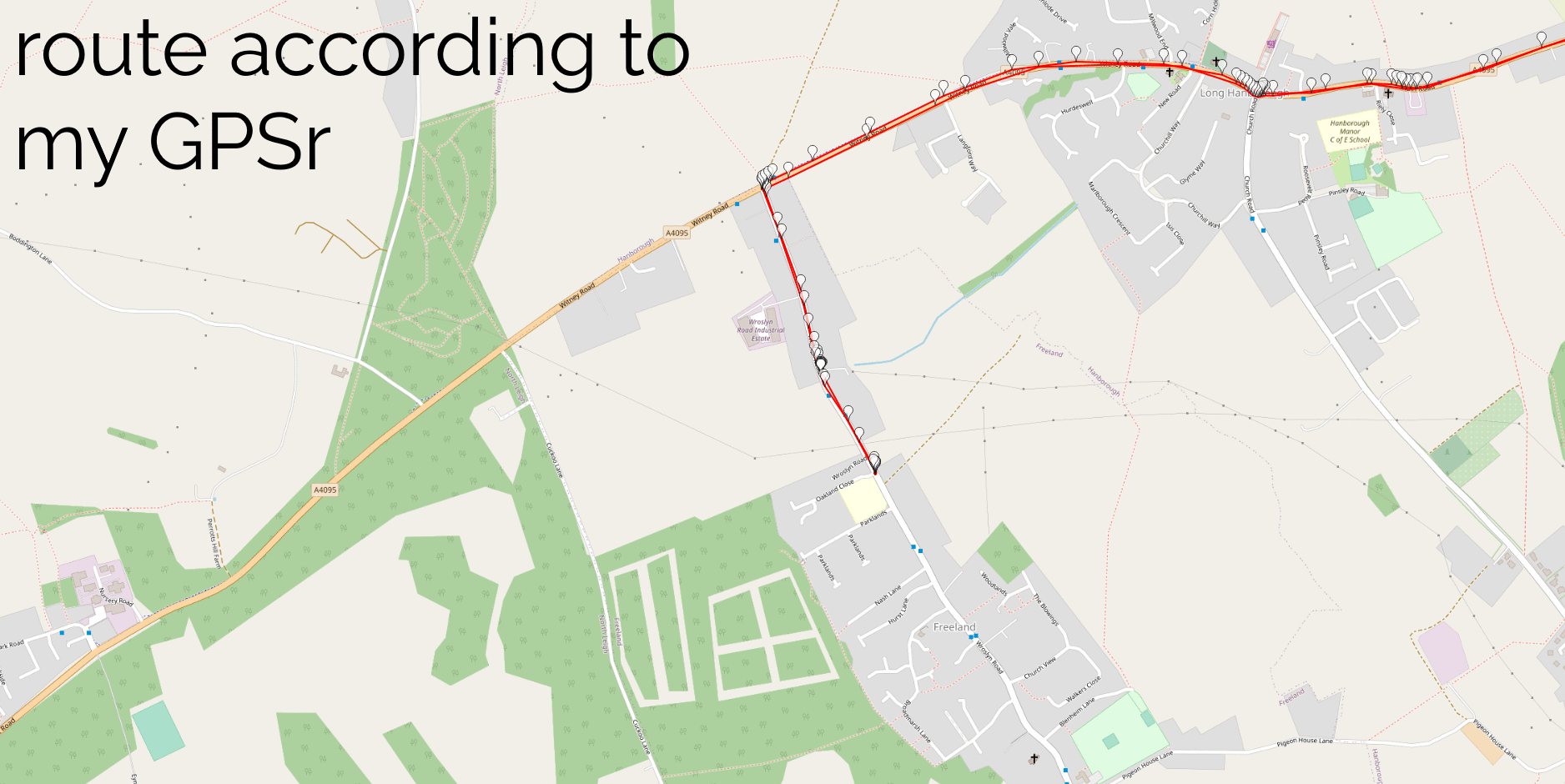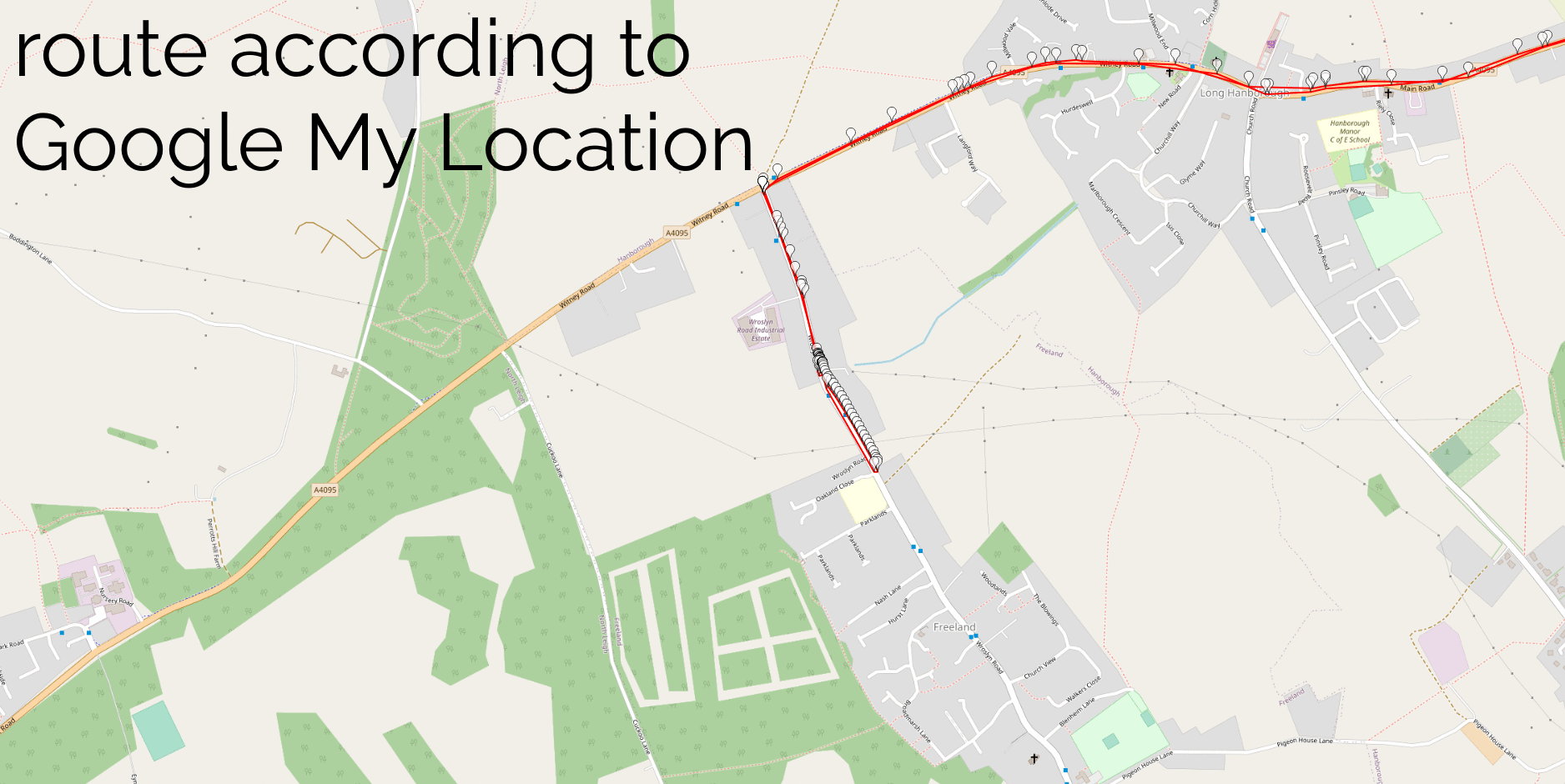
I assumed that my algorithm would detect all of my actual geohash finds, and yes: all of these appeared as-expected in my results. This was a good confirmation that my approach worked.
And, crucially: about a dozen additional candidate points showed up in my search. Most of these – listed at the end of this post – were 50m+ away from the hashpoint and involved me driving or cycling past on a nearby road… but one hashpoint stuck out.
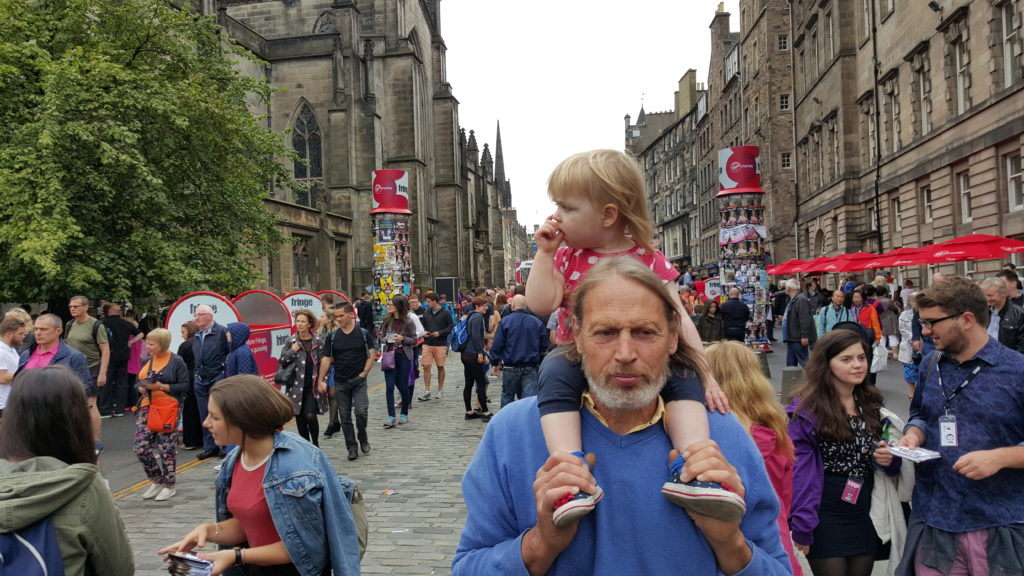

In August 2015 we took a trip up to Edinburgh to see a play of Ruth‘s brother Robin‘s. I don’t remember much about the play because I was on keeping-the-toddler-entertained duty and so had to excuse myself pretty early on. After the play we drove South, dropping Tom off at Lanark station.
We exited Lanark via the Hyndford Bridge… which is – according to the map – tantalisingly-close to the 2015-08-22 55 -3 hashpoint: only about 23 metres away!
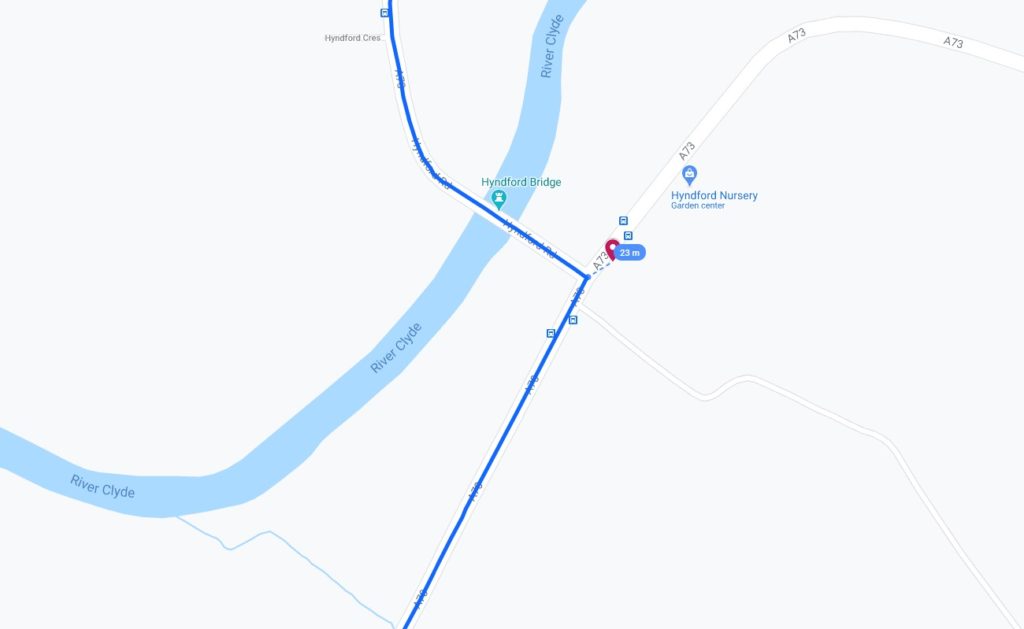
That doesn’t feel quite close enough to justify retroactively claiming the geohash, tempting though it would be to use it as a vehicle to my easy geohash ribbon. Google doesn’t provide error bars for their exported location data so I can’t draw a circle of uncertainty, but it seems unlikely that I passed through this very close hashpoint.
Pity. But a fun exercise. This was the nearest of my near misses, but plenty more turned up in my search, too:

This is a repost promoting content originally published elsewhere. See more things Dan's reposted.
How far ahead of Apple Maps is Google Maps?
Over the past year, we’ve been comparing Google Maps and Apple Maps in New York, San Francisco, and London—but some of the biggest differences are outside of large cities.
Take my childhood neighborhood in rural Illinois. Here the maps are strikingly different, and Apple’s looks empty compared to Google’s:
Similar to what we saw earlier this year at Patricia’s Green in San Francisco, Apple’s parks are missing their green shapes. But perhaps the biggest difference is the building footprints: Google seems to have them all, while Apple doesn’t have any.
…
This link was originally posted to /r/outside. See more things from Dan's Reddit account.
The original link was: http://i.imgur.com/sYVlwjk.png
This link was originally posted to /r/todayilearned. See more things from Dan's Reddit account.
The original link was: http://web.archive.org/web/20070509182328/http://www.nst.com.my/Current_News/nst/Wednesday/National/20070328080627/Article/local1_html
MALAYSIA will not ask Google Earth to blur images of the country’s military facilities to avoid terrorist attacks. Defence Minister Datuk Seri Najib Razak said doing so would indirectly pin-point their location anyway.
“The difference in, or lack of, pixelation of images of the military facilities compared to the surrounding areas will make it easy for visual identification.” In his written reply to Datuk Dr James Dawos Mamit (BN-Mambong), Najib said the images were provided worldwide commercially.…
After a few years break, I’m once again heading up to Edinburgh for the Fringe Festival. As on previous ocassions, I expect to spend a lot of time enjoying Peter Buckley Hill‘s Free Fringe, which is just about the best thing to happen to the Fringe ever. And this time, I’m going to be better-prepared than ever. I’ve made a map.
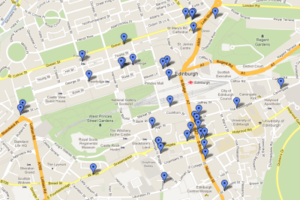
Sharing is caring, so I’ve made the map available to you, too. Click on the picture to see the map. Because it’s in Google Maps it ought to work on your mobile phone. If you’ve got GPS then you can get lost in Edinburgh in high-tech ways you never before thought possible. Click on any given venue for a web address where you can find a list of events that are occurring at that venue.
Or if you’re really nerdy, you can download the KML and go geocaching-for-comedy. Just me? Okay then…
Update: you can now view the map on the frontpage of the Free Fringe website, too.
It’s like stepping back in time through videogaming history. And also sideways, into a parallel universe of knights and dragons.

It’s like Google Maps, but in the style of retro top-down, turn-based RPGs. It’s really quite impressive: it’s presumably being generated at least semi-dynamically (as it covers the whole world), but it’s more than a little impressive. It sometimes makes mistakes with rivers – perhaps where their visibility from the air is low – but nonetheless an interesting feat from a technical perspective.
There’s “8-bit Street View”, too.
Nice one, Google. Go take a look.