I love feeds!
Maybe you’ve heard already, but I love RSS.
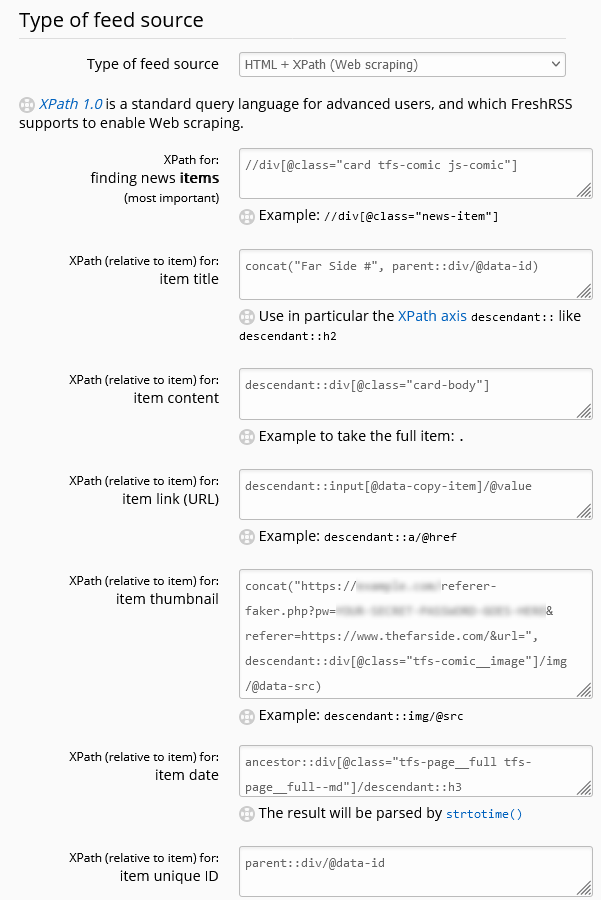
I love it so much that I retrofit sites without feeds into it for the convenience of my favourite reader FreshRSS: working around (for example) the lack of feeds in The Far Side (twice), in friends’ blogs, and in my URL shortener. Whether tracking my progress binging webcomic history, subscribing to YouTube channels, or filtering-out sports news, feeds are the centre of my digital life.

There’s been a bit of a resurgence lately of sites whose only subscription option is email, or – worse yet – who provide certain “exclusive” content only to email subscribers.
I don’t want to go giving an actual email address to every damn service, because:
- It’s not great for privacy, even when (as usual) I use a unique alias for each sender.
- It’s usually harder to unsubscribe than I’d like, and rarely consistent: you need to find a recent message, click a link, sometimes that’s enough or sometimes you need to uncheck a box or click a button, or sometimes you’ll get another email with something to click in it…
- I rarely want to be notified the very second a new issue is published; email is necessarily more “pushy” than I like a subscription to be.
- I don’t want to use my email Inbox to keep track of which articles I’ve read/am still going to read: that’s what a feed reader is for! (It also provides tagging, bookmarking, filtering, standardised and bulk unsubscribing tools, etc.)
So what do I do? Well…
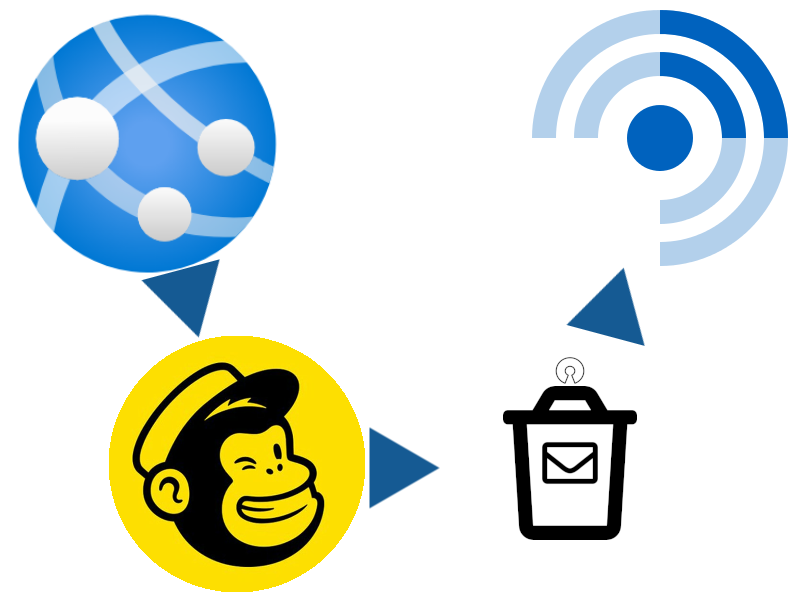
I already operate an OpenTrashMail instance for one-shot throwaway email addresses (which I highly recommend). And OpenTrashMail provides a rich RSS feed. Sooo…
How I subscribe to newsletters (in my feed reader)
If I want to subscribe to your newsletter, here’s what I do:
- Put an email address (I usually just bash the keyboard to make a random one, then put @-a-domain-I-control on the end, where that domain is handled by OpenTrashMail) in to subscribe.
- Put
https://my-opentrashmail-server/rss/the-email-address-I-gave-you/rss.xmlinto my feed reader. - That’s all. There is no step 3.
Now I get your newsletter alongside all my other subscriptions. If I want to unsubscribe I just tell my feed reader to stop polling the RSS feed (You don’t even get to find out that I’ve unsubscribed; you’re now just dropping emails into an unmonitored box, but of course I can resubscribe and pick up from where I left off if I ever want to).
Obviously this approach isn’t suitable for personalised content or sites for which your email address is used for authentication, because anybody who can guess the random email address can get the feed! But it’s ideal for those companies who’ll ocassionally provide vouchers in exchange for being able to send you other stuff to your Inbox, because you can simply pipe their content to your feed reader, then add a filter to drop anything that doesn’t contain the magic keyword: regular vouchers, none of the spam. Or for blogs that provide bonus content to email subscribers, you can get the bonus content in the same way as the regular content, right there in a folder of your reader. It’s pretty awesome.
If you don’t already have and wouldn’t benefit from running OpenTrashMail (or another trashmail system with feed support) it’s probably not worth setting one up just for this purpose. But otherwise, I can certainly recommend it.










![Browser debugger running document.evaluate('//li[@class="blog__post-preview"]', document).iterateNext() on Beverley's weblog and getting the first blog entry.](https://bcdn.danq.me/_q23u/2022/09/debugger-select-from-xpath-1024x256.png)