Parenting is about sacrifices.
Here, I’m making the noble sacrifice of forcing myself to drink a delicious beer so my 10-year-old can use the customer-only bathroom at a beachside amateur football club. Such a sacrifice.
This checkin to GCAG598 Mimetic - Passeig de Gràcia reflects a geocaching.com log entry. See more of Dan's cache logs.
QEF for the geokid and I while exploring beautiful Barcelona this wet weekend. Greetings from Oxford, UK. TFTC!
Here in my hotel room, high above Barcelona, I woke up. It was still dark outside, so I looked to my phone – sitting in its charging cradle – as a bedside clock. It told me that the time was 02:30 (01:30 back home), and that the sun would rise at 07:17.
But how long would it be, until then?
Daylight savings time is harmonised across Europe by EU Directive 2000/84/EC1, but for all the good this harmonisation achieves it does not perfectly remove every ambiguity from questions like this. That it’s 02:30 doesn’t by itself tell me whether or not tonight’s daylight savings change has been applied!
It could be 00:30 UTC, and still half an hour until the clocks go back, or it could be 01:30 UTC, and the clocks went back half an hour ago. I exist in the “hour of uncertainty”, a brief period that happens once every year2. Right now, I don’t know what time it is.
I remember when it first started to become commonplace to expect digital devices to change their clocks twice a year on your behalf. You’d boot your PC on a morning and it’d pop up a dialog box to let you know what it had done: a helpful affordance that existed primarily, I assume, to discourage you from making the exact same change yourself, duplicating the effort and multiplying the problem. Once, I stayed up late on last Saturday in March to see what happened if the computer was running at the time, and sure enough, the helpful popup appeared as the clocks leapt forward, skipping over sixty minutes in an instant, keeping them like leftovers to be gorged upon later.
Computers don’t do that for us anymore. They still change their clocks, but they do it silently, thanklessly, while we sleep, and we generally don’t give it a second thought.
That helpful dialog that computers used to have had a secondary purpose. Maybe we should bring it back. Not as a popup – heaven knows we’ve got enough of those – but just a subtle subtext at the bottom of the clock screens on our phones. “Daylight savings: clock will change in 30 minutes” or “Daylight savings: clock changed 30 minutes ago”. Such a message could appear for, say, six hours or so before and after our strange biannual ritual, and we might find ourselves more-aware as a result.
Of course, I suppose I could have added UTC to my world clock. Collapsed the waveform. Dispelled the ambiguity. Or just allowed myself to doze off and let the unsleeping computers do their thing while I rested. But instead I typed this, watching as the clock reached 02:59 and then to 02:00. I’d started writing during summertime; I’d finished after it ended, a few minutes… earlier?
Daylight savings time remains a crazy concept.
1 Why yes, I am the kind of nerd who didn’t have to look that up. Why do you ask?
2 In places that observe a one-hour shift for summertime.
There’s a pretty, lightweight, short-sleeved shirt that I own. If you know me personally, it’s reasonably likely you’ll have seen me wearing it at some point.
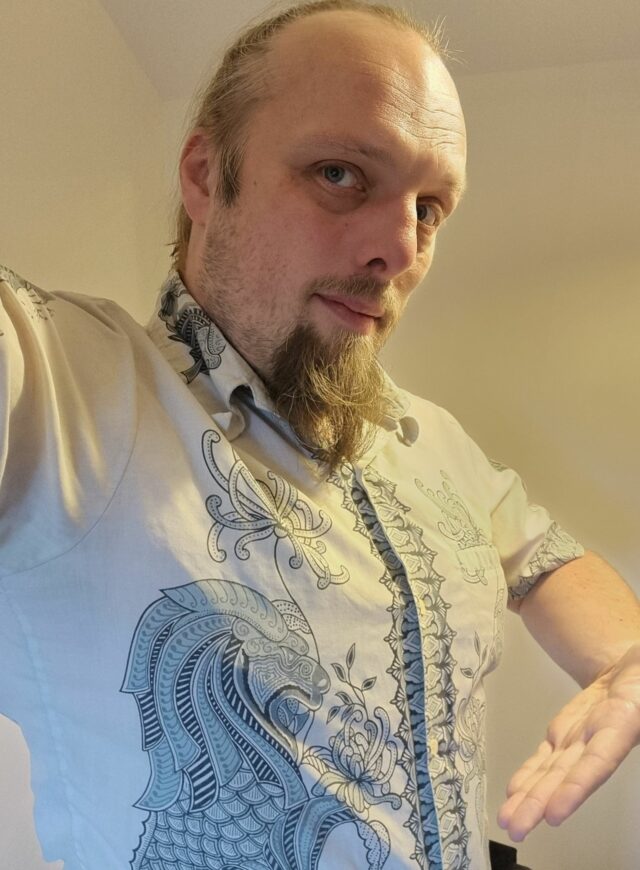

And I’m confident that it’s the oldest piece of clothing I own. I first got it in the winter of 2001/2002, which makes it a massive 23 years old!
Given that I seem to be incapable of owning clothing without holing it in short order1, why has this shirt lasted so long? Is it imbued with some form of mystical draconic longevity?2
A 23-year-old shirt that’s been worn most months would most-likely already represent good value, but I bought this particular garment second-hand, from a stall in Preston’s Covered Market. For 50 pence! That’s cheap enough that it would have been the best-value shirt I’d ever owned even if it had fallen apart as quickly as my clothes do typically.
That it’s instead lasted over two decades is just… mind-boggling.
1 My socks wear holes within a year or two; my trousers gain crotch tears, possibly as a result of over-aggressive cycling, within a similar timespan; my t-shirts for some reason reliably get holes under the left armpit usually within four years, and so on.
2 With thanks to the Wayback Machine, I found an original web page about my shirt on the designer’s website (in an example of full “early 2000s” web design – look at those image navigation buttons with no alt-text! – as well as other retro touches like being able to order by fax before paying in deutschemarks). They’re still making shirts, I see, although no longer in this design.
This post is also available as a podcast. Listen here, download for later, or subscribe wherever you consume podcasts.
Right in time for International Crisp Sandwich Day (St. Crispin’s Day) tomorrow, I’ve taught myself to enjoy Pickled Onion Monster Munch.

There’s a need for somebody… anybody… to eat Pickled Onion Monster Munch in our household, because we have a bit of an oversupply. In order to reliably get both of the other flavours that people like (Roast Beef and Flamin’ Hot, respectively), we end up buying multipacks that also contain Pickled Onion flavour, and these unwanted extras pile up in the snack cupboard until we happen to have a houseguest that we can palm them off onto.

My entire life, I’ve claimed not to like pickled onion flavour crisps. As a kid, I would only eat salt & vinegar and ready salted flavours, eventually expanding my palate into “meaty” flavours like chicken and roast beef (although never, absolutely never, prawn cocktail). Later, I’d come to also enjoy cheese & onion and variants thereof, and it’s from this that I realise that I’m probably being somewhat irrational.
Because if you think about it: if you want to make a “pickled onion” flavour crisp, what flavouring ingredients would you use? It turns out that most crisp manufacturers use a particular mixture of (a) the ingredient that makes salt & vinegar crisps taste “vinegary” and (b) the ingredient that makes cheese & onion crisps taste “onioney”. So in summary:

Maybe that deliberate and conscious thought process is all I need? Maybe that’s it, and just having gone through the reasoning, I will now like pickled onion crisps!
Conveniently, I have a cupboard in my kitchen containing approximately one billion packets of Pickled Onion Monster Munch. So let’s try it out.
It turns out they’re okay!
They’re not going to dethrone either of the other two flavours of Monster Munch that we routinely restock on, but at least now I’m in a position where I can do something about our oversupply.
And all it took was stopping to think rationally about it. If only everything were so simple.
This checkin to geohash 2024-10-22 51 -1 reflects a geohashing expedition. See more of Dan's hash logs.
Harcourt Hill Bridleway, between Cumnor and North Hinksey
I’m on sabbatical from work right now, so I’m hoping to be able to get out to this hashpoint while the kids are at school.
After dropping the kids off at school, the geopup/hashhound and I set out for the hashpoint. Coming up the “short side” of the bridleway from Botley would be a shorter walk, but we opted to park in Cumnor and come up the “long side” of Harcourt Hill to avoid Oxford’s traffic (and the inevitable fee for parking on the city’s side of the hill).
Harcourt Hill (like my village of Stanton Harcourt) doubtless gets its name from the Harcourt Family, who supported William the Conqueror during his conquest of Great Britain back in 1066 and were ultimately granted huge swathes of land around this part of the world in recognition of their loyalty. To this day, you find “Harcourt” in a lot of place names in this neck of the woods.
The hashpoint was so easy to find, we almost walked right over it: it’s right in the centre of the footpath/bridleway. Even my dog, who often doesn’t like long walks or muddy paths, didn’t get a chance to complain before we got there. We arrived at 09:35 and took the requisite photos, which can be found below. We also kept a GPS tracklog and vlogged our experience, all of which you can see below.
I’ve not properly hashed in a long while, so it was great to get back out there!
My GPSr kept a tracklog.
Also available via YouTube.





Six or seven years ago our eldest child, then a preschooler, drew me a picture of the Internet1. I framed it and I keep it on the landing outside my bedroom – y’know, in case I get lost on the Internet and need a map:
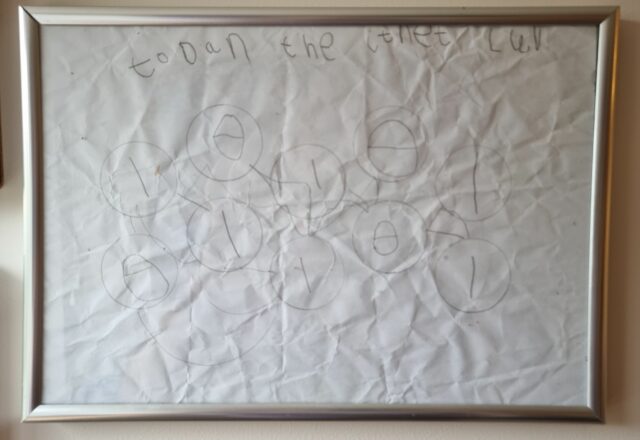

I found myself reminded of this piece of childhood art when she once again helped me with a network map, this weekend.
As I kick off my Automattic sabbatical I’m aiming to spend some of this and next month building a new server architecture for Three Rings. To share my plans, this weekend, I’d been drawing network diagrams showing my fellow volunteers what I was planning to implement. Later, our eldest swooped in and decided to “enhance” the picture with faces and names for each server:
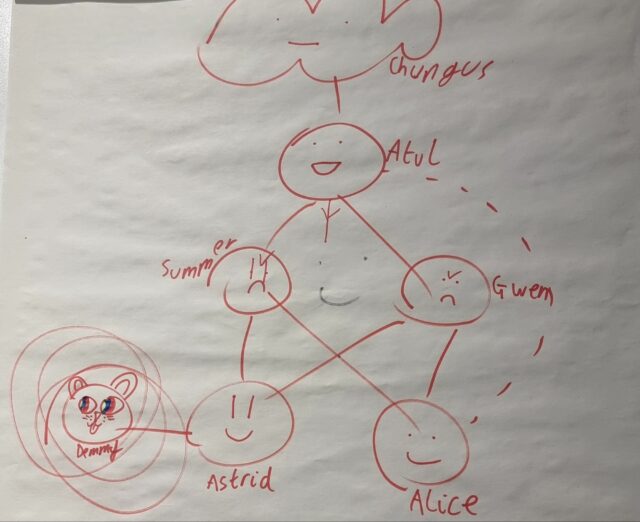
I noted that she named the read-replica database server Demmy2, after our dog.

It’s a cute name for a server, but I don’t think I’m going to follow it. The last thing I want is for her to overhear me complaining about some possible future server problem and misinterpret what I’m saying. “Demmy is a bit slow; can you give her a kick,” could easily cause distress, not to mention “Demmy’s dying; can we spin up a replacement?”
I’ll stick to more-conventional server names for this new cluster, I think.
Day #2 of my sabbatical had a morning in which I’ve mostly been roped into some charity-related digital forensics… until I got distracted by dndle.app, which apparently I accidentally broke yesterday! Move Fast and Fix Things!
Kicking off day #1 of my three-month sabbatical from work at a hotel in Reading, at a meeting with fellow Three Rings volunteers to discuss our organisational culture and values.
The Beeb continue to keep adding more and more non-news content to the BBC News RSS feed (like this ad for the iPlayer app!), so I’ve once again had to update my script to “fix” the feed so that it only contains, y’know, news.