Adam Koszary – whom I worked alongside at the Bodleian – the social media specialist who brought the “absolute unit” meme to the masses, started blogging earlier (again?) this year. Yay!
But he’s completely neglected to put an RSS feed on hew new blog. Boo!

I’ve talked at length about how I use FreshRSS‘s “XPath Scraping” feature (for Bev’s blog, Far Side, Forward, new Far Side, and Vmail, among others), but earlier this week somebody left a comment to ask me more about how I test and debug my XPath scrapers. Given that I now need to add one for Adam’s blog, I’m in a wonderful position to walk you through it!
Setting up and debugging your FreshRSS XPath Scraper
Okay, so here’s Adam’s blog. I’ve checked, and there’s no RSS feed1, so it’s time to start planning my XPath Scraper. The first thing I want to do is to find some way of identifying the “posts” on the page. Sometimes people use
solid, logical id="..." and class="..." attributes, but I’m going to need to use my browser’s “Inspect Element” tool to check:
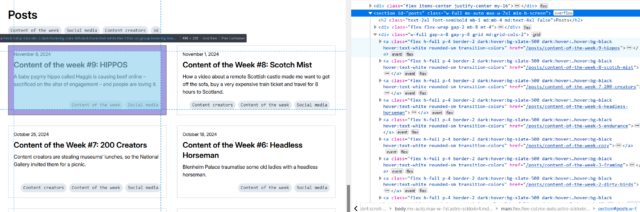
The next thing that’s worth checking is that the content you’re inspecting is delivered with the page, and not loaded later using JavaScript. FreshRSS’s XPath Scraper works with the raw HTML/XML that’s delivered to it; it doesn’t execute any JavaScript2, so I use “View Source” and quickly search to see that the content I’m looking for is there, too.

$x(...), to which you can path a string containing an XPath query and get back a NodeList of the element.
First, I’ll try getting all of the links inside the #posts section by running
![A browser's debug console executes $x('//*[@id="posts"]//a') , and gets 14 results.](https://bcdn.danq.me/_q23u/2024/11/adam-k-xpath-1-640x188.png)
/posts/, so I filtered my query down to

Obviously, this link points to the full post, so that tells me I can put ./@href as the “item link” attribute in FreshRSS.
Next, it’s time to see what other metadata I can extract from each post to help FreshRSS along:
Inspecting the post titles shows that they’re <h3>s. Running
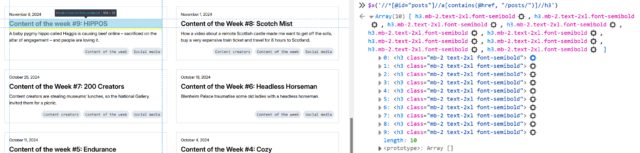
Inspecting within the post summary content, it’s… not great for scraping. The elements class names don’t correspond to what the content is4: it looks like Adam’s using a utility class library5.
Everything within the <a> that we’ve found is wrapped in a <div class="flex-grow">. But within that, I can see that the date is
directly inside a <p>, whereas the summary content is inside a <p> within a <div class="mb-2">. I don’t want my code to
be too fragile, and I think it’s more-likely that Adam will change the class names than the structure, so I’ll tie my queries to the structure. That gives me
descendant::div/p for the date and descendant::div/div/p for the “content”. All that remains is to tell FreshRSS that Adam’s using F j, Y as his
date format (long month name, space, short day number, comma, space, long year number) so it knows how to parse those dates, and the feed’s good.
If it’s wrong and I need to change anything in FreshRSS, the “Reload Articles” button can be used to force it to re-load the most-recent X posts. Useful if you need to tweak things. In
my case, I’ve also set the “Article CSS selector on original website” field to article so that the full post text can be pulled into my reader rather than having to visit
the actual site. Then I’m done!
Takeaways
- Use Inspect Element to find the elements you want to scrape for.
- Use
$x( ... )to test your XPath expressions. - Remember that most of FreshRSS’s fields ask for expressions relative to the news item and adapt accordingly.
- If you make a mistake, use “Reload Articles” to pull them again.
Footnotes
1 Boo again!
2 If you need a scraper than executes JavaScript, you need something more-sophisticated. I used to use my very own RSSey for this purpose but nowadays XPath Scraping is sufficient so I don’t bother any more, but RSSey might be a good starting point for you if you really need that kind of power!
3 If you’ve not had the chance to think about it before: View Source shows you the actual HTML code that was delivered from the web server to your browser. This then gets interpreted by the browser to generate the DOM, which might result in changes to it: for example, invalid elements might be removed, ambiguous markup will have an interpretation applied, and so on. The DOM might further change as a result of JavaScript code, browser plugins, and whatever else. When you Inspect Element, you’re looking at the DOM (represented “as if” it were HTML), not the actual underlying HTML
4 The date isn’t in a <time> element nor does it have a class like
.post--date or similar.
5 I’ll spare you my thoughts on utility class libraries for now, but they’re… not positive. I can see why people use them, and I’ve even used them myself before… but I don’t think they’re a good thing.
