A few weeks ago, my credit card provider wrote to me to tell me that they were switching me back from paperless to postal billing because I’d “not been receiving their emails”.
This came as a surprise to me because I have been receiving their emails. Why would they think that I hadn’t?

Turns out they have a tracking pixel in their email to track that it’s been opened, as well as potentially additional data such as when it was opened (or re-opened), what email client or clients the recipient uses, what IP address or addresses they read their mail from, and so on.
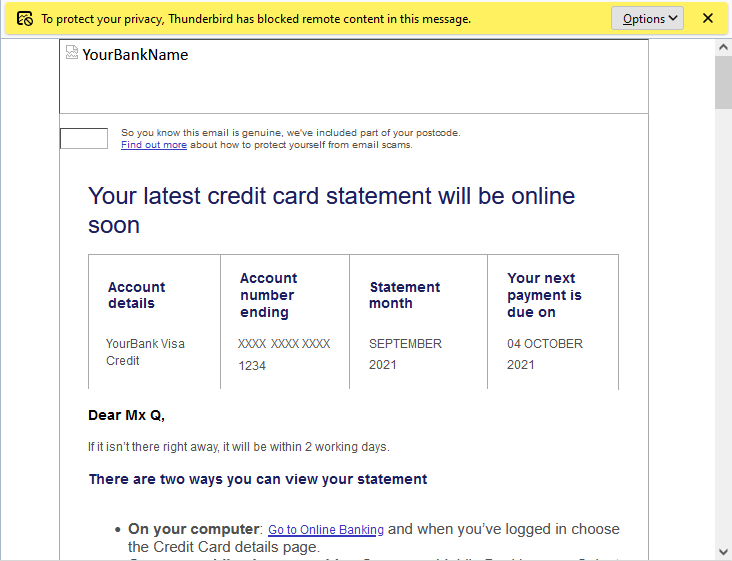
Naturally, because I don’t like creepy companies tracking what I do on my own computers and try to minimise how much they can do so, I read most of my mail with remote content disabled:
Jeremy just had something to say on this topic, too, based on his recent reading of Design for Safety by Eva PenzeyMoog:
Do you have numbers on how many people opened a particular newsletter? Do you have numbers on how many people clicked a particular link?
You can call it data, or stats, or analytics, but make no mistake, that’s tracking.
Follow-on question: do you honestly think that everyone who opens a newsletter or clicks on a link in a newsletter has given their informed constent to be tracked by you?
Needless to say, I had words with my credit card provider. Paperless billing is useful to almost everybody but it’s incredibly useful for blind and partially-sighted users (who are also the ones least-likely to have images loading in the first place, for obvious reasons) because your computer can read your communication to you which is much more-convenient than a letter. Imagine how annoyed you’d be if your bank wrote you a letter (which you couldn’t read but had to get somebody else to read to you) to tell you that because you don’t look at the images in their emails they’re not going to send them to you any more?
Even if you can somehow justify using tracking technologies (which don’t work reliably) to make general, statistical decisions (“fewer people open our emails when the subject contains the word ‘overdraft’!”), you can’t make individual decisions based on them. That’s just wrong.