This is a repost promoting content originally published elsewhere. See more things Dan's reposted.
Undeniably one of the most obscure and unusual 'wars' in history, this is the story of how the killing of an escaped pig almost caused a war between the United States and Britain.
‘The Pig War’ is perhaps one of the most obscure and unusual wars in history. The story begins back in 1846 when the Oregon Treaty was signed between the US and Britain. The treaty aimed to put to rest a long standing border dispute between
the US and British North America (later to be Canada), specifically relating to the land between the Rocky Mountains and the Pacific coastline.
The Oregon Treaty stated that the US / British American border be drawn at the 49th parallel, a division which remains to this day. Although this all sounds rather straightforward,
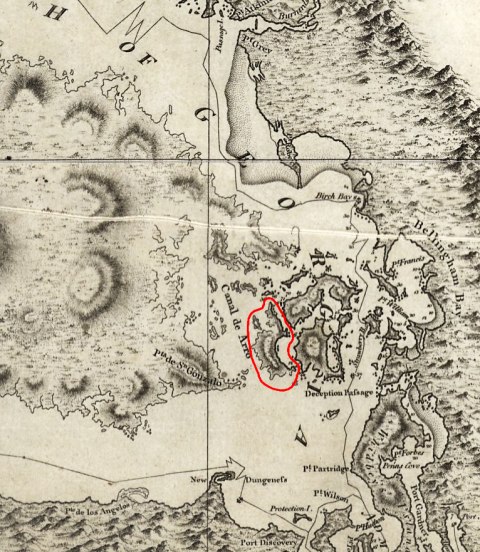
the situation because slightly more complicated when it came to a set of islands situated to the south-west of Vancouver. Around this region the treaty stated that the border be
through ‘the middle of the channel separating the continent from Vancouver’s Island.’ As you can see from the map below, simply drawing a line through the middle of
the channel was always going to be difficult due to the awkward positioning of the islands.
…
This is a repost promoting content originally published elsewhere. See
more things Dan's reposted.
The long read: Every baffled new parent goes searching for answers in baby manuals. But what they really offer is the reassuring fantasy that life’s most difficult questions have
one right answer
Human beings are born too soon. Within hours of arriving in the world, a baby antelope can clamber up to a
wobbly standing position; a day-old zebra foal can run from hyenas; a sea-turtle, newly hatched in the sand, knows how to find its way to the ocean. Newborn humans, on the other
hand, can’t hold up their own heads without someone to help them. They can’t even burp without assistance. Place a baby human on its stomach at one day old – or even three
months old, the age at which lion cubs may be starting to learn to hunt – and it’s stranded in position until you decide to turn it over, or a sabre-toothed tiger strolls into
the cave to claim it. The reason for this ineptitude is well-known: our huge brains, which make us the cleverest mammals on the planet, wouldn’t fit through the birth canal if
they developed more fully in the womb. (Recently,
cognitive scientists have speculated that babies may actually be
getting more useless as evolution proceeds; if natural selection favours ever bigger brains, you’d expect humans to be born with more and more developing left to do.)
This is why humans have “parenting”: there is a uniquely enormous gap between the human infant and the mature animal. That gap must be bridged, and it’s difficult to resist
the conclusion that there must be many specific things adults need to get right in order to bridge it. This, in turn, is why there are parenting advice manuals – hundreds and
hundreds of them, serving as an index of the changing ways we have worried about how we might mess up our children.
…
