Among Twitter’s growing list of faults over the years are various examples of its increasing divergence from open Web standards and developer-friendly endpoints. Do you remember when you used to be able to subscribe to somebody’s feed by RSS? When you could see who follows somebody without first logging in? When they were still committed to progressive enhancement and didn’t make your browser download ~5MB of Javascript or else not show any content whatsoever? Feels like a long time ago, now.
But those complaints aside, the thing that bugged me most this week was how much harder they’ve made it to programatically get access to things that are publicly accessible via web pages. Like avatars, for example!
If you’re a human and you want to see the avatar image associated with a given username, you can go to twitter.com/that-username and – after you’ve waited
a bit for all of the mandatory JavaScript to download and run (I hope you’re not on a metered connection!) – you’ll see a picture of the user, assuming they’ve uploaded one and not made
their profile private. Easy.
If you’re a computer and you want to get the avatar image, it used to be just as easy; just go to
twitter.com/api/users/profile_image/that-username and you’d get the image. This was great if you wanted to e.g. show a Facebook-style facepile of images of people who’d retweeted your content.
But then Twitter removed that endpoint and required that computers log in to Twitter, so a clever developer made
a service that fetched avatars for you if you went to e.g. twivatar.glitch.com/that-username.
But then Twitter killed that, too. Because despite what they claimed 5½ years ago, Twitter still clearly hates developers.
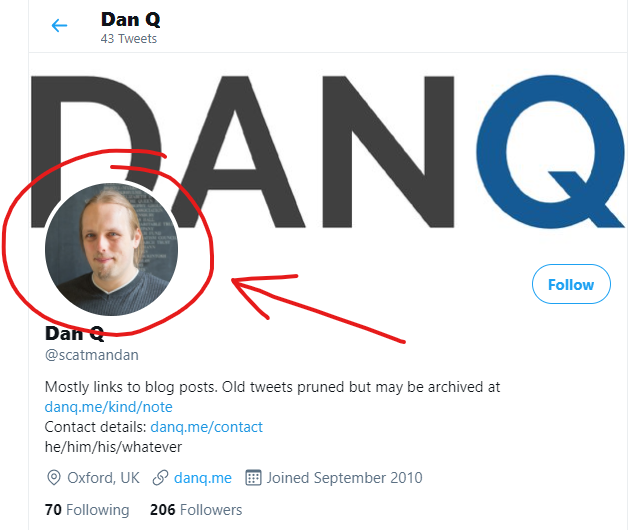
Recently, I needed a one-off program to get the avatars associated with a few dozen Twitter usernames.
First, I tried the easy way: find a service that does the work for me. I’d used avatars.io before but it’s died, presumably because (as I soon discovered) Twitter had made
things unnecessarily hard for them.
Second, I started looking at the Twitter API documentation but it took me in the region of 30-60 seconds before I said “fuck that noise” and decided that the set-up overhead in doing things the official way simply wasn’t justified for my simple use case.
So I decided to just screen-scrape around the problem. If a human can just go to the web page and see the image, a computer pretending to be a human can do exactly the same. Let’s do this:
/* Copyright (c) 2021 Dan Q; released under the MIT License. */ const Puppeteer = require('puppeteer'); getAvatar = async (twitterUsername) => { const browser = await Puppeteer.launch({args: ['--no-sandbox', '--disable-setuid-sandbox']}); const page = await browser.newPage(); await page.goto(`https://twitter.com/${twitterUsername}`); await page.waitForSelector('a[href$="/photo"] img[src]'); const url = await page.evaluate(()=>document.querySelector('a[href$="/photo"] img').src); await browser.close(); console.log(`${twitterUsername}: ${url}`); }; process.argv.slice(2).forEach( twitterUsername => getAvatar( twitterUsername.toLowerCase() ) );
Obviously, using this code would violate Twitter’s terms of use for automation, so… don’t, I guess?
Given that I only needed to run it once, on a finite list of accounts, I maintain that my approach was probably kinder on their servers than just manually going to every page and saving the avatar from it. But if you set up a service that uses this approach then you’ll certainly piss off somebody at Twitter and history shows that they’ll take their displeasure out on you without warning.
$ node get-twitter-avatar.js alexsdutton richove geohashing TailsteakAD LilFierce1 ninjanails
alexsdutton: https://pbs.twimg.com/profile_images/740505937039986688/F9gUV0eK_200x200.jpg
lilfierce1: https://pbs.twimg.com/profile_images/1189417235313561600/AZ2eLjAg_200x200.jpg
richove: https://pbs.twimg.com/profile_images/1576438972/2011_My_picture4_200x200.jpeg
geohashing: https://pbs.twimg.com/profile_images/877137707939581952/POzWWV2d_200x200.jpg
ninjanails: https://pbs.twimg.com/profile_images/1146364466801577985/TvCfb49a_200x200.jpg
tailsteakad: https://pbs.twimg.com/profile_images/1118738807019278337/y5WWkLbF_200x200.jpg
But it works. It was fast and easy and I got what I was looking for.
And the moral of the story is: if you make an API and it’s terrible, don’t be surprised if people screen-scape your service instead. (You can’t spell “scraping” without “API”, amirite?)